I’m walking through the latest beta version of Agile Web Development with Rails 2nd Edition, specifically the new bits on deploying Rails apps. Capistrano – the preferred and recommended deployment utility. Thing is – Capistrano hinges on Subversion. Not something covered in AWDwR or appropriate to be covered. There’s plenty of other books on the subject.
Though, that left me stuck on how to set up a Subversion repository and access it.
- It's not Mac OS X native, but you can give Eclipse's SVN client a try. It works on Mac OS X, and it's pretty good.
- Google; About Google; Privacy; Terms.
- Th svnX open-source GUI client for Mac OS X provides support for most features of the standard svn client, including working with local working copies as well as a useful remote repository browser. It supports all Subversion versions from 1.4 through to 1.7 and is the best open-source GUI Subversion client for Mac OS.
- Your email must be between 3 and 100 characters long and look like an e-mail address.
I do my hosting at TextDrive, and in the interest of making this process just a hair simpler, I set up my svn repository there. Here’s how I did it:
- Set up repository on TextDrive domain in
webmin.[your-server].textdrive.com:80.
There’s a ‘subversion repository’ menu option right when you sign-in. - Assign svn access rights to a TextDrive domain user.
It’s a radio button and select list selection in their profile. - Install Subversion on your local Mac – I did via macports
- Install svnX and in svnX preferences, confirm your path to svn in svnX (macports uses
/opt/local/bin) - Import your project into the TextDrive repository
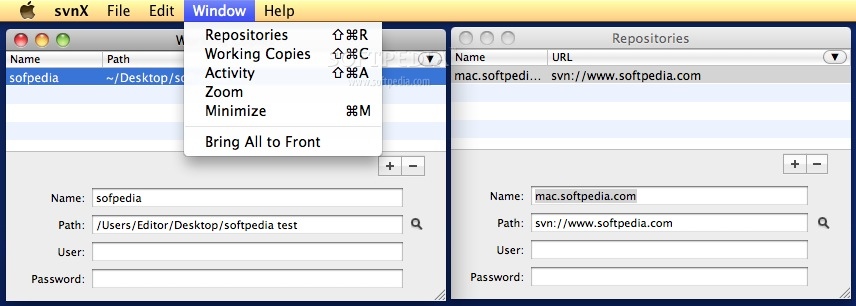
svn import /Users/your/local/path/to/the/app http://[your-domain]/svn/[repository-name]/ -m 'initial import' --username=[your-svn-account-name] - Connect svnX to the repository
Path:http://[your-domain]/svn/[your-repository-name]
User:[your-svn-user-name]
Pass:[your-svn-user-name-pass] - Check out your project back on to your mac by clicking the ‘svn
export‘ button and picking a directory to put it (not your original directory). I created an/svndirectory within my main project directory. - Now, if everything worked, double-clicking the repository should load it up in a new window.
- I’ve got a weird proxy between me and the internet right now, so I’ll make sure the commits work tomorrow. UPDATE: Yep, it works. Yah!
Trusted Mac download svnX 2.0.016960. Virus-free and 100% clean download. Get svnX alternative downloads.
svnX is a free Cocoa GUI for Mac OS X ! |
Subversion is a version control system that is a compelling replacement for CVS in the open source community.
The easiest way to install Subversion for OS X is to use Martin Ott's binary packages.
From the official web site :
Features of Subversion
Most current CVS features
Subversion is meant to be a better CVS, so it has most of CVS's features. Generally, Subversion's interface to a particular feature is similar to CVS's, except where there's a compelling reason to do otherwise.
Svnx For Mac Latest Version
Directories, renames, and file meta-data are versioned
Lack of these features is one of the most common complaints against CVS. Subversion versions not only file contents and file existence, but also directories, copies, and renames. It also allows arbitrary metadata ('properties') to be versioned along with any file or directory, and provides a mechanism for versioning the `execute' permission flag on files.
Commits are truly atomic
No part of a commit takes effect until the entire commit has succeeded. Revision numbers are per-commit, not per-file; log messages are attached to the revision, not stored redundantly as in CVS.
Apache network server option, with WebDAV/DeltaV protocol
Subversion can use the HTTP-based WebDAV/DeltaV protocol for network communications, and the Apache web server to provide repository-side network service. This gives Subversion an advantage over CVS in interoperability, and provides various key features for free : authentication, path-based authorization, wire compression, and basic repository browsing.
Standalone server option
Subversion also offers a standalone server option using a custom protocol (not everyone wants to run Apache 2.x). The standalone server can run as an inetd service, or in daemon mode, and offers basic authentication and authorization. It can also be tunnelled over ssh.
Svnx For Mac Os
Branching and tagging are cheap (constant time) operations
There is no reason for these operations to be expensive, so they aren't.
Branches and tags are both implemented in terms of an underlying 'copy' operation. A copy takes up a small, constant amount of space. Any copy is a tag; and if you start committing on a copy, then it's a branch as well. (This does away with CVS's 'branch-point tagging', by removing the distinction that made branch-point tags necessary in the first place.)
Natively client/server, layered library design
Subversion is designed to be client/server from the beginning; thus avoiding some of the maintenance problems which have plagued CVS. The code is structured as a set of modules with well-defined interfaces, designed to be called by other applications.
Client/server protocol sends diffs in both directions
The network protocol uses bandwidth efficiently by transmitting diffs in both directions whenever possible (CVS sends diffs from server to client, but not client to server).
Costs are proportional to change size, not data size
In general, the time required for an Subversion operation is proportional to the size of the changes resulting from that operation, not to the absolute size of the project in which the changes are taking place.This is a property of the Subversion repository model.
Efficient handling of binary files
Svnx For Mac Catalina
Subversion is equally efficient on binary as on text files, because it uses a binary diffing algorithm to transmit and store successive revisions.
Parseable output
Svnx For Mac Apple Store
All output of the Subversion command-line client is carefully designed to be both human readable and automatically parseable; scriptability is a high priority.